Before I begin discussing the Strive Score, let me note that I’m not a doctor or any other type of accredited authority. I’m just an ordinary Pelotoner who likes data. This blog should not be used in place of advice from a real medical expert.
On April 30th, 2021, Peloton announced a new heart rate-related metric across all workouts. They call it “Strive Score” and here’s how they describe it:
Strive Score is a personal, non-competitive metric that measures your performance in every workout—from equipment to the floor. All you need is a compatible heart rate monitor…and some good old-fashioned motivation.
Peloton PR
The Holy Grail, not just for Peloton but for all on-and-offline fitness programs is finding some way to quantify effort in a way that is meaningful regardless of your personal physiology and fitness level. This sort of universal measurement has so far eluded sports science, and is a huge barrier in the automation of any sort of personalized training program. Some day, when science has evolved sufficiently, we will look back at the sort of metrics we use today as being very crude, but nevertheless today this is what we have to work with.
Peloton’s best metric in this regard is the good ol’ FTP number. FTP, Functional Threshold Power, is a number which is arrived at by actual experimentation on the athlete. Basically, to find your FTP score, you work as hard as you possibly can for a period of time, and however much work you can do (a multiplier might be involved depending on how long your test is) becomes your FTP. Your workout intensity is then based on that number (10 minutes at 80% FTP, 5 minutes at 110% of FTP, etc). Periodically, you re-test to recalibrate, and use the new FTP number as the basis of future workouts.
The Strive Score explained
Many people do not want to endure the FTP test, and that’s understandable. Unfortunately, if you’re not going to be using a benchmark that was at least arrived at using real-world data about you individually, you really have no choice but to fall back to something that is far more generic. This is where heart rate comes into the picture. Heart rate correlates to effort, of course. Your heart rate is slowest during most phases of sleep, and is highest when doing strenuous work such as running or climbing stairs. We’re all individuals when it comes to how quickly our heart rate increases under stress and how quickly it recovers when resting, but it’s generally safe to say that you’re generally working harder when your heart rate is higher, and working less hard when it is lower.
The Strive Score seeks to quantify heart rate over time. Even sitting still you’ll generate a strive score value over time (at a rate of about 0.0048 points per second), as long as your heart is beating. The longer you go, the higher the score rises (so a ten minute effort at constant heart rate will yield double the score of a five minute effort at the same heart rate). Raising your heart rate above a certain percentage of your maximum heart rate* triggers a bonus multiplier (starting at 2x for heart rates above 65% of maximum).
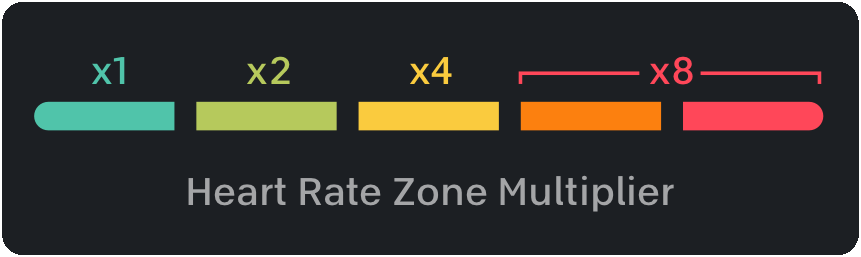
Since the heart rate multiplier and time are the only variables, it is fairly easy to calculate the theoretical minimums and maximums of the Strive Score, and they are as follows**:
| Minutes | Minimum | Maximum |
| 5 | 1.4 | 11.6 |
| 10 | 2.9 | 23.2 |
| 15 | 4.3 | 34.8 |
| 20 | 5.8 | 46.4 |
| 30 | 8.7 | 69.6 |
| 45 | 13 | 104.4 |
| 60 | 17.4 | 139.2 |
| 90 | 26.1 | 208.8 |
Note that the strive score is incremented every second, so you will not be able to hit the max score for an interval unless your heart rate is the maximum zone going into it.
Reading the table: The table above lists the minimum and maximum attainable values for the indicated duration. For example, if your heart is beating, you cannot get less than a 1.4 score in five minutes of exercise, because you will be in zone 1 the entire time. If your heart rate is in zone 4 or above for the entire five minutes, your five-minute maximum would be 11.6 points. If you effort is not strictly zone 1 or zone 4+, your strive score will be somewhere between these minimums and maximums, depending on how many seconds you spend in each zone.
Strive Score or FTP, which is best?
I think I can say without fear of contradiction that the FTP test result, if arrived at after a valid test, is the best available metric of fitness available to us. It’s what I use to track my own fitness, and I rely on it more than I do heart rate or Strive Score.
Another nice thing about FTP is that it is not a Peloton concept, but rather it is used in other areas of sport. Zwift has a very nice feature to calculate FTP, for example.
All that said in favor of the FTP, the Strive Score has one very intriguing feature that FTP lacks, and that it is intended to be an indicator of effort rather than an indicator of achievement. As your fitness improves, it actually becomes easier and easier to hit your FTP numbers (which is why you need to re-test and re-calibrate periodically), because FTP is a measure of achievement, and when you’re fitter you can achieve more (or, in this case, achieve the same with less effort). Strive Score, as a measure of effort, should be less affected by your relative fitness (though it is, to some extent). For people seeking to improve their fitness, and who are looking to get some sort of feedback that they’re putting in the right amount of effort (at least, as compared to other attempts), the Strive Score could be a useful metric for that sort of information.
* Maximum heart rate is estimated using age.
** The per-second strive point value of 0.00483 was arrived at through experimentation. Please let me know if you get markedly different results, and I will try to refine this value. I confess that I expected to find it to be a “rounder” number, such as 0.005, but it doesn’t actually seem to be quite that high.

Leave a Reply